What this blog covers:
- What is a Universal Semantic Layer and how does it work?
- How can you build a universal semantic layer to handle any scale of future data?
- How can Kyvos help with a semantic layer powered by our Smart OLAP™ technology?
The concept of the semantic layer is almost as old as the BI tools themselves. Earlier, each BI tool had its own semantic layer and was used by specific teams within the enterprise. Those were the days of data silos and moderate data volumes. However, as volumes increased, enterprises began to consolidate all their data on modern data platforms while business users continued to use their existing, familiar BI tools. Multiple versions of business logic in each BI tool often led to different interpretations of the same data. And, that’s why it became important to create a single data view or semantic layer across BI tools and business teams. Before we discuss why you need a semantic layer and how you can build one that can handle future data workloads, let us first understand what it means.
What is a Universal Semantic Layer?
“Semantic” is an ancient Greek word that signifies the relationship between words, phrases, signs, and symbols to give it some meaning. In terms of enterprise data, it means utilizing the relationship between schema, tables, and columns in a data warehouse or data lake to create a very simple business view that hides the complexity of the underlying data, and delivers a consistent view of the dimensions, measures, and hierarchies that you can use for analysis on the Semantic data platform.
A smart semantic layer is a layer of abstraction that provides a consistent way of interpreting data. It maps complex data into familiar business terms so that users across the enterprise can access the same source of truth, with full confidence in its integrity. The idea is to get all the definitions and business logic in one place and then manage and change them centrally. The basic purpose of the semantic layer is to make data more useful to the business and simplify querying for the users.
Why do you need a Universal Semantic Layer?
Think about all the data that lands in your data lake each day. How do you make sense of that data? For a business user who needs to analyze all that data, it’s hard to figure out how to even start querying. Without a semantic data model, it is difficult for the user to identify the correct customer key, customer ID, or the date hierarchy. Different fields can mean different things to different people. Each team or user would then interpret those fields in different ways and get potentially different views of the same data.
Most BI tools allow users to define their own semantic models – the dimensions, the measures, and the hierarchies. One option is to let the business users create their own semantic models in the tools that they use. However, achieving a single source of truth is difficult in this case. It is necessary to have a common representation of data so that different teams can access their data using common business terms.
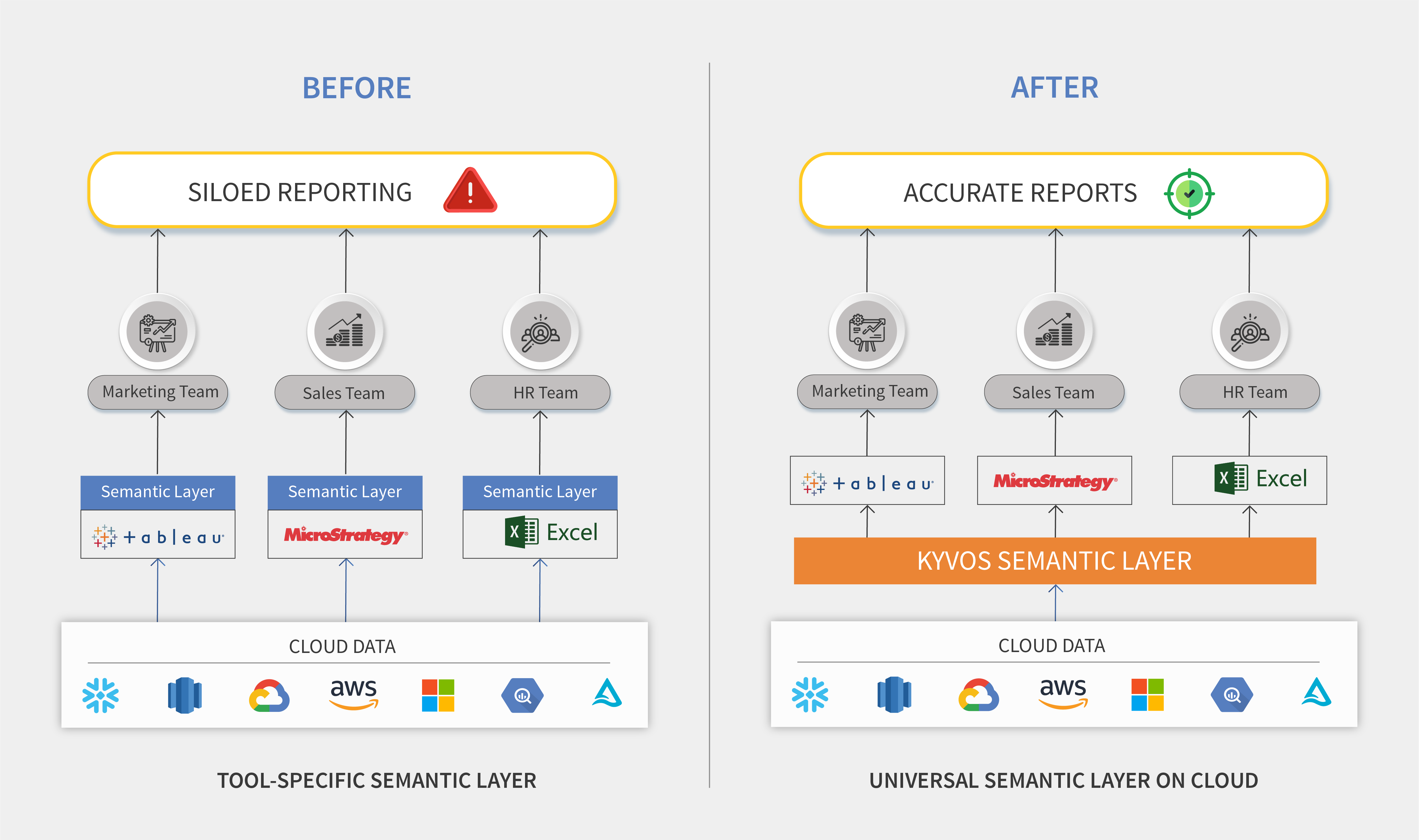
Once you create a universal semantic layer, the same model is available to all business users regardless of the BI tool they use. They can work on Excel, Tableau, MicroStrategy, Looker or any other tool they like, and access the same semantic model. In addition, Kyvos also has an in-built data visualization tool. This helps create a consistent view of data for users across the enterprise.
Besides consistency, another key factor is simplicity. A smart semantic layer on the cloud simplifies the user’s interaction with data and makes it easy for them to identify the areas they want to explore. Fields that need to be exposed to the business users are identified and given meaningful names that make sense to the business users. The dimensions, the measures, and the hierarchies are defined centrally. Users can then drag and drop these dimensions and measures in their charts and reports without worrying about the complexity of the data that lies underneath. When complex data is presented in an easily understandable way, it promotes data usage and encourages more teams to use the available data.
How to Build a Universal Semantic Layer that can Handle Future Data Workloads?
Enterprises today have more data available for analysis and reporting than they ever had. As a result, the amount of effort that users need to put in to analyze this data has also increased phenomenally. Trends indicate that in the future, volumes will grow further, data complexity will increase, and the number of data sources will rise, and all of this at a much faster rate. Therefore, it is important to build a universal semantic layer that provides a consistent data view as well as has the power to handle your current and future data workloads.
Imagine a complex data scenario with millions of cardinalities, hundreds of dimensions and measures, and trillions of rows of data. You need a mechanism to handle that kind of data and create a simplistic view of it. This is where Kyvos comes in.
Kyvos builds a universal semantic layer that can handle any scale or complexity of data and meet the growing analytical needs of an enterprise. Powered by smart OLAP technology, the Kyvos semantic layer:
- Enhances information in the data lake and makes it more useful for the business
- Makes it easier for users to query massive data on the cloud and on-premise storage platforms
- Accelerates query performance on massive data
Best Way to Create a Universal Semantic Layer
There are multiple layers between the source data and the point where the data is made available for analysis. The source data layer is the physical database or the data lake. The Kyvos universal semantic layer is a layer of abstraction built on the source data where all the metadata is defined so that the model gets enriched and becomes simple enough for the business user to understand.
Dataset relationships that form the basis for semantic modeling are defined first. The user does not have to worry about the relationship diagram as it is defined by the designer who understands the underlying data. Next, comes the cube design where the dimensions, the measures, the attributes, and the hierarchies are defined. Once the cube is built, users can view the dimensions and measures that are available to them in their BI tool. They can drag and drop them into their charts and reports and start querying instantaneously.
Unlike most solutions, the Kyvos universal semantic layer is a full-featured layer that enhances the data by adding hierarchies and calculated measures. You can define all kinds of hierarchies, such as multiple hierarchies, alternate hierarchies, parent-child hierarchy, different ways of aggregating, custom roll-up, and more. Once the semantic data model is complete, users can query and drill down through a hierarchy in a consistent way. However, if you are dealing with complex data and massive volumes, it is not just enough to build a semantic layer.
Not Just a Semantic Layer; There’s More
Most enterprises face performance issues after they build their semantic models. Slow response times are a major deterrent when users fire complex queries on massive volumes of data. The next thing they need is high performance as the semantic data model by itself does not deliver performance. It just provides consistency and simplicity.
The Kyvos universal semantic layer is powered by smart OLAP technology that delivers unmatched performance on massive data. The semantic model hides the complexity of the data, and the cube supports the semantic model by delivering instant response times for all queries. As all the combinations are processed in advance, the Kyvos cube delivers high performance for both warm as well as cold queries across hundreds of dimensions and measures. Users can slice and dice, or drill down based on the semantic model and get quick answers to all their questions.
Another key advantage of Kyvos is that it leverages the scale and flexibility of cloud platforms and on-premise data lakes for querying and building the cubes. As a result, it can deliver sub-second response times even for trillions of rows. This kind of performance cannot be achieved at this scale with partial aggregation or in-memory solutions.
Benefits of Semantic Layer
It’s time to adopt the semantic layer in your cloud BI architecture to resolve data volume and complexity issues while empowering users to achieve a single standard for consuming and driving enterprise-wide analytics. Some benefits of having a semantic layer are:
Performance and Scale – Kyvos’ Smart Semantic Layer™ is designed to handle the scale and complexity issues of your data. A semantic model hides data’s physical complexity from business users while its OLAP capabilities deliver exceptionally high performance.
Security and Governance – Kyvos provides a native three-tiered security architecture that ensures data protection at multiple levels. It builds a semantic layer between the enterprise data storage system and BI tool to enable granular-level access control through row and column level security at the group and user levels.
Single Source of Truth – Kyvos’ Smart Semantic Layer™ on your Cloud BI architecture bridges the gap between complex data sources and business users by centralizing and standardizing their data logic. It helps businesses access a single source of truth; they can analyze years of historical data with sub-second response times.
Simplifies Analytics Stack – Having a semantic layer architecture in your analytics stack empowers data analysts, business users, and data engineers to use their data logically and make intelligent and accurate business decisions. Instead of thinking of it as an extension to your current architecture, think of it as a solution that can simplify your analytics stack.
Industries That Benefit from Kyvos’ Universal Semantic Layer
A universal semantic layer can facilitate data-centric decision-making across industries by addressing scale, speed, and performance issues for smarter and faster analytics. Industries that can primarily benefit from our revolutionary technology are:
Banking and Financial Services (BFSI): Strict regulations and compliance requirements make BFSI teams more focused with data visibility to always have a big-picture view. However, legacy applications with siloed information and disparate data sources make it challenging to access as much data as needed for comprehensive financial analytics.
Kyvos’ semantic layer helps aggregate this data and add common business logic to it so that finance experts can make faster decisions with full trust in the integrity of these insights. With this unified data view on time, they can prevent financial risks and avoid non-compliance issues.
Retail Sector: With most industries processing massive amounts of data for complete digital transformation, retailers can’t afford to be left behind. In fact, retail companies collect and analyze omnichannel data to improve customer experiences amid growing competition.
The transaction-level information makes it difficult to gain actionable insights, especially when it comes in huge volumes and is accessed by multiple users concurrently. Thankfully, our semantic layer helps get a 360-degree view across the channels, products, and verticals for end-to-end data visibility. The layer lets you use any existing BI tool for interactive access to data residing on the cloud or on-premises.
Telecommunications: As media viewership patterns get complex and personalized, predictive analytics becomes complex. Delayed insights can further complicate matters. Modern data platforms can capture real-time information to understand viewing patterns and analyze this data against user demographics, behaviors, and social media interactions.
However, despite this infrastructure, BI tools are not always capable of handling day-to-day granular queries, or the users lack the expertise to work on these tools. The Kyvos semantic layer architecture allows analysts to use modern data platforms while still working with their favorite tools.
Kyvos leverages existing cloud or on-prem platforms for storing smart aggregates while minimizing cost and maintenance overheads. With no data movement, the platform maintains security at the data storage layer and offers instant insights into billions of rows of viewership data.
Looking Ahead
As data complexity and volumes increase, it becomes increasingly important to build a universal semantic layer so that your business users get a consistent view of all enterprise data and can conduct quick analysis on it. Once you get all your data together and build a semantic layer on it, you enable full, consistent, and quick access to a single source of truth. This ensures that when one team talks about a particular dimension, then everybody across the enterprise refers to the same thing. Having a high-performant semantic layer in place will allow your business users to take advantage of the data more quickly to get actionable insights from all their data.
FAQs
What does a semantic layer do?
A smart semantic layer is a layer of abstraction that provides a consistent way of interpreting data. It maps complex data into familiar business terms so that users across the enterprise can access the same source of truth, with full confidence in its integrity.
What is semantic layer in data lake?
There are multiple layers between the source data and the point where the data is made available for analysis. The source data layer is the physical database or the data lake. The universal semantic layer is a layer of abstraction built on the source data where all the metadata is defined so that the model gets enriched and becomes simple for the business user to understand.
What is an example of a semantic layer?
Kyvos universal semantic layer is a full-featured example. It improves data accessibility and analytics for unmatched performance on massive data. The model hides the data complexity, and Kyvos’ patented smart pre-aggregation supports the semantic model by delivering instant response times for all queries.
What is the difference between a metric store and a semantic layer?
As an abstraction layer between data sources and end-user applications or programs, a semantic layer offers a unified data view for simplified and consistent querying across the data sources, irrespective of their underlying location or structure. On the other hand, a metric store works as a centralized repository to store and manage raw, numerical data (operational statistics and performance metrics) for monitoring and analytics.
What is the purpose of a semantic layer?
In a universal semantic layer, the same model is available to all business users regardless of the BI tool they use. They can work on any other tool and access the same semantic model. Kyvos also has an in-built data visualization tool to create a consistent view of data for users across the enterprise. The layer simplifies a user’s interaction with data and makes it easy to identify the areas they want to explore.



